Virtual Machine Network Modes
This section describes bridged and host-routed network modes for virtual machines.
Bridged Mode for Virtual Machines
By default, a new virtual machine is created with a network adapter that operates in the bridged mode. The figure below demonstrates an example network configuration where two virtual machines, VM #1 and VM #2, are configured to work in the bridged mode.
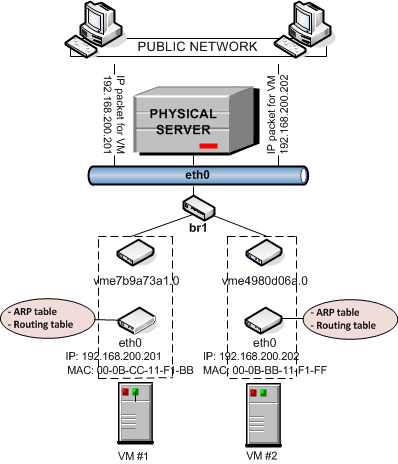
In this configuration:
-
Each virtual machine has a separate virtual adapter that exposes two interfaces: (1) an
ethXinterface in the virtual machine (eth0in the figure) and avmeinterface on the server (vme7b9a73a1.0andvme4980d06a.0in the figure). Both interfaces are closely linked to each other, which means that an IP packet entering one interface always comes out from the other one. Anethadapter has a MAC address, can be assigned one or more IP addresses, belong to different network environments, and so on.Note: To simplify things, virtual adapters operating in the bridged mode are called
vmeadapters, though it is not quite correct from the technical point of view. - VM #1 and VM #2 keep their own ARP and routing tables that they consult when sending or receiving data.
-
The virtual adapters of both virtual machines are bridged through the bridge
br1to the physical network adaptereth0. -
All outgoing data packets are sent from the virtual machines through the bridge and
eth0physical adapter to the destination, according to their routing tables. -
All incoming data packets for VM #1 and VM #2 reach the
eth0physical adapter first and are then transmitted through the bridge to thevmeinterface of the destination virtual machine.
Host-Routed Mode for Virtual Machines
The other network mode a virtual machine can work in is the host-routed mode. The figure below demonstrates an example network configuration where two virtual machines, VM #1 and VM #2 , are set to operate in the host-routed mode.
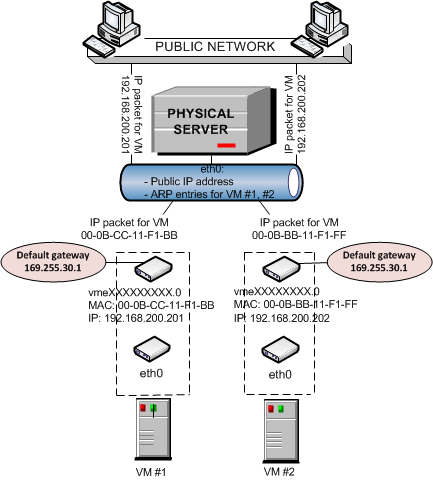
In this configuration:
-
Each virtual machine also has a virtual adapter exposing two interfaces: an
ethXinterface in the virtual machine and avmeXinterface on the server. -
Unlike the bridged mode, the ARP entries for VM #1 and VM #2 are stored on the server rather than in the virtual machines themselves. The server creates these ARP entries and saves them to its ARP table when VM #1 and VM #2 start. You can use the
arp -ncommand to view the current ARP entries on a server, for example:# arp -n
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.30.0.4 ether 00:1a:e2:c7:17:c1 C eth0
10.30.23.162 ether 70:71:bc:42:f6:a0 C eth0
192.168.200.201 * * MP eth0
192.168.200.202 * * MP eth0
-
Along with ARP entries, the server also creates routing entries for both virtual machines. So when the server receives a data packet destined for IP address 192.168.200.201, it knows that the packet must be forwarded to the
vmeXXXXXXXX.0interface of VM #1. -
The server handles all incoming traffic for both virtual machines. Consider the following situation:
- Computer X on the network wants to send a data packet to VM #1 with IP address 192.168.200.201, so it issues an ARP request which computer has this IP address.
- The server replies with its own MAC address.
- Computer X sends the data packet to the indicated MAC address.
-
The
eth0physical adapter receives the packet and routes it to thevmeinterface of VM #1.
-
All outgoing network traffic sent from VM #1 and VM #2 are routed through the default gateway to the
eth0adapter on the server. The default gateway for host-routed virtual machines is automatically assigned the IP address of 169.255.30.1. This special IP address is taken from the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) range and used exclusively to deliver data packets from virtual machines to the server.
|
|
 Feedback
Feedback
|