Container Network Modes
This section describes bridged and host-routed network modes for Containers.
Note: IPSec connections inside Containers are supported.
Host-Routed Mode for Containers
By default, a new Container starts operating in the host-routed mode. In this mode, the Container uses a special network adapter,
venet0
, to communicate with the server where it resides, with the other Containers on the server, and with computers on external networks. The figure below demonstrates an example network configuration where all Containers are set to work in the host-routed mode.
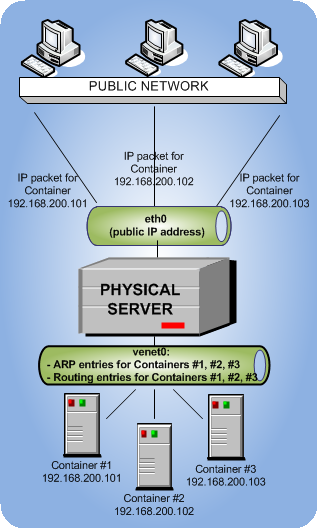
In this configuration:
-
Container #1, Container #2, Container #3
use the
venet0adapter as the default gateway to send and receive data to/from other networks. They also use this adapter to exchange the traffic among themselves. -
When
Container #1, Container #2,
and
Container #3
start, the server creates ARP and routing entries for them in its ARP and routing tables. You can view the current ARP and routing entries on a server using the
arp -nandroute -ncommands. For example:# arp -n
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.30.0.4 ether 00:1a:e2:c7:17:c1 C eth0
10.30.23.162 ether 70:71:bc:42:f6:a0 C eth0
192.168.200.101 * * MP eth0
192.168.200.102 * * MP eth0
192.168.200.103 * * MP eth0
# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.200.101 * 255.255.255.255 UH 1000 0 0 venet0
192.168.200.102 * 255.255.255.255 UH 1000 0 0 venet0
192.168.200.103 * 255.255.255.255 UH 1000 0 0 venet0
10.30.0.0 * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
default parallels.com 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
As you can see, the ARP and routing tables contain entries about IP addresses 192.168.200.101, 192.168.200.102, and 192.168.200.103 that belong to Containers #1, #2, and 3#.
Note: The server also stores ARP and routing tables for Containers that have the offline management feature enabled even if they are not running. For more on this feature, see Configuring Offline Management .
-
All Container outgoing network traffic goes to the
venet0adapter and is forwarded via theeth0physical adapter to the destination, according to the routing table of the server. -
All Container incoming network traffic is also processed by the
venet0adapter. Consider the following situation:- Computer X on the local network wants to send a data packet to Container #1 with IP address 192.168.200.101, so it issues an ARP request which computer has this IP address.
- The server hosting Container #1 replies with its MAC address.
- Computer X sends the data packet to the indicated MAC address.
-
The server receives the packet and transmits it to
venet0that forwards the packet to Container #1.
Bridged Mode for Containers
The default network adapter of a Container can operate in the host-routed mode only. You can, however, create additional virtual adapters in Containers and make them operate in the bridged network mode. The following figure shows an example network configuration where Container #1 and Container #2 are set to work in the bridged mode.
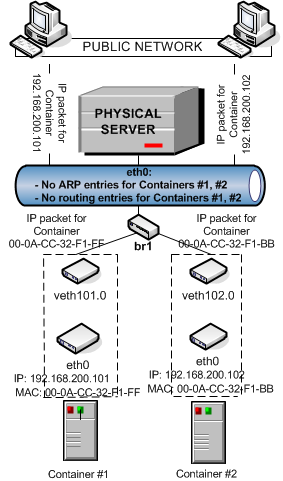
In this configuration:
-
Container #1 and Container #2 have separate virtual adapters consisting of two network interfaces:
- An ethX interface in the Container (eth0 in the figure). This interface represents a counterpart of a physical network adapter installed on a standalone server. Like any other physical adapter, it has a MAC address, can be assigned one or more IP addresses, included in different networks, and so on.
-
A vethX interface on the Hardware Node
(veth101.0
and
veth102.0
in the figure). This interface is mostly used to maintain the communication between the Hardware Node and Ethernet interfaces in Containers.
Note: To simplify things, virtual adapters operating in the bridged mode are called
vethadapters, though it is not quite correct from the technical point of view.
Both interfaces are closely linked to each other, so a data packet entering one interface always comes out from the other one.
- Container #1 and Container #2 keep their own ARP and routing tables that they consult when sending or receiving data.
-
The
vethadapters of both Containers are bridged through the bridgebr1to the physical network adaptereth0. -
All Container outgoing traffic comes via the
vethadapters to the bridge and are then transmitted through theeth0physical adapter to the destination, according to the routing tables stored in the Containers. -
All incoming data packets for Container #1 and Container #2 reach the
eth0physical adapter first and are then sent through the bridge to thevethadapter of the destination Container.
|
|
 Feedback
Feedback
|